CC:
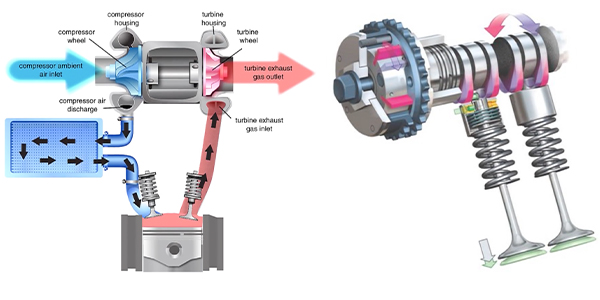
There are a lot of turbocharged cars and light-duty trucks on the road today. And this trend is expected to continue in the coming years. This will provide ample opportunities for you and your shop to diagnose and repair turbocharger systems on a variety of makes and models. Symptoms of a faulty turbocharger may include loss of power, abnormal whistling noises, excessive smoke, high fuel consumption, overheating, high exhaust temperature and oil leaks from the turbo.
But it’s important to note that defects in other components can produce these same symptoms. Before condemning the turbocharger, remember that turbo performance can only be impaired by mechanical damage or blockage caused by debris. When searching for the source of a boost leak, start with a thorough visual inspection of the charge air pipes and hoses, with the engine off, of course. A ruptured hose may appear to be intact, so squeeze, pull and twist them as needed to locate that source of leak.
Look for evidence of rubbing or contact between the charge air pipes and hoses with neighboring components. Look for any clamps which may have worked their way loose or were improperly installed during a previous repair. Special tools are available which allow you to use regulated shop air to build system pressure and locate the leak. This is a safe and effective method for simulating boost pressure with the engine off, similar to pressurizing a coolant circuit with the cooling system pressure tester.
Do not attempt to build boost by power breaking the engine. This is a dangerous practice, which can cause excessive heat to build up in the engine bay and could lead to a crash. There are a number of things to consider if you are replacing a failed turbocharger. If the bearings failed and debris was carried into the intake system, you must replace or clean all of the effective components.
Certain manufacturers require that the intake manifold is replaced in the event of a turbocharger failure. The risk of metal debris being trapped inside the manifold is too high. It is not worth the chance of later engine failure to try and save some money. It’s also a good idea to inspect the catalytic converter for any signs of damage or debris. If you are replacing a failed turbocharger, it is best practice to replace the turbocharger coolant and oil lines as well.
Engine oil and coolant are critical to the turbocharger. If the hoses or lines are damaged, clogged, contaminated or faulty, they can lead to premature turbocharger failure. Some oil feed lines may contain screens or filters inside them, which can trap metal debris and lead to oil starvation. Before installing a new turbocharger, add a small amount of clean engine oil into the oil feed port. The ideal practice is to hook up the oil feedline, disable the engine from starting and then crank the engine until oil comes out of the oil drain tube.
This will prevent it from dry starting the first time you start the engine. We recommend checking that the PCV and oil separator circuits are both functioning properly. Turbocharger kits, like this one from Standard, make replacement a little easier. They already include the required gaskets and hardware needed. Standard’s turbo program also includes things like turbo boost sensors and solenoids, speed sensors, turbo cooler lines, oil drain tubes and oil lines, as well as charge air coolers. Most importantly, ensure that the customer is aware of the maintenance schedule for their vehicle. This includes regular oil changes, using the correct oil, air filter replacement, as well as fuel system cleaning, or walnut blasting, to remove carbon buildups from the intake valves. As with all vehicle systems, proper maintenance is the secret to maximum turbocharger service life. I’m Brian Sexton. Thanks for watching.
This video is sponsored by Standard Motor Products.