CC:
Turbocharged gasoline engines continue to grow in popularity and it’s happened quickly. According to the Department of Energy, approximately 1% of all 2000 model year light-duty vehicles were turbocharged. Fast-forward to today, and over one-third of all light-duty vehicles are now turbocharged. So why the rapid change? Fuel economy standards. Current cafe standards call for automakers to increase the average fuel economy of their lineups to 54.5 miles per gallon by 2025. Turbocharging is just one method being used to boost the fuel economy in modern vehicles. It allows them to build engines which produce more power with less displacement and sometimes with fewer cylinders.
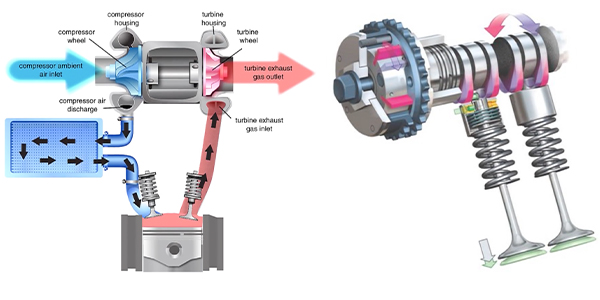
How does a turbocharger work? Let’s talk about it in simple terms. Gasoline engines burn a mixture of air and fuel. The engine can only draw in a fixed amount of air on its own, so the ECU controls the amount of fuel added to the combustion chamber to maintain that optimum air and fuel mixture. Turbochargers can increase the air flow into the engine. This means more fuel can be added, and the engine can make more power.
Inside the turbocharger, you’ll see a shaft with a turbine wheel on one end and a compressor wheel on the other. The turbine is driven by exhaust gases leaving the engine. This spins the compressor wheel, which forces more air into the intake manifold. This increased air flow and pressure is known as boost or charge air. The charge air typically passes through an inner cooler or heat exchanger. This helps to remove some of the heat and makes the air denser. The air then travels to the combustion chamber.
Turbochargers rely heavily on one under-hood fluid, engine oil. Engine oil is critical for the bearings inside the turbocharger. Without proper lubrication, these bearings simply will not last. Some turbos will also have engine coolant circulated through the turbocharger to help keep temperatures in check. Restricted flow of either of these fluids can very quickly lead to failure.
The most common customer concern would likely be whistling noises coming from the engine bay, along with reduced engine power. These are typically indicators of charge air leaking from a connection somewhere in the system. A smoke machine can be used to help you find the source of a leak. Other signs of a failed turbo include reduced engine power and reduced fuel economy.
Some turbos operate at temperatures in excess of 1700 degrees and can spin at 150,000 RPM to 200,000 RPM. So the components used inside a turbo charger matter. The rotating journal and thrust bearings used in Standard turbochargers are 100% quality tested. In fact, every Standard turbocharger is end-of-line tested throughout the full RPM range. When you install a Standard turbocharger, you can be confident that you are installing a part which has been tested and will perform for both you and your customer.
Best of all, Standard turbocharger kits include the gaskets and hardware needed for a complete turbo repair. Standard’s turbo program also includes related components like the actuators, turbo boost sensors and solenoids, wastegate solenoids, bypass valves, speed sensors, turbo coolant lines, oil drain tube, and oil lines, as well as charge air coolers. I’m Brian Sexton. Thanks for watching.
This video is sponsored by Standard Motor Products.